
Table of Contents
ToggleTesting in cotton Fabric Preparation
Textile Processing

In textile Processing, to get best quality textiles of international standards, one need
to have the international standard testing methods. Textile
products have to undergo different testing to meet quality
standard and to maintain customer satisfactions.
Here are some of the standard test methods which are
commonly used by fabric pretreatment industries.
1.Test of Effective Desizing
2.Test of Effective Scouring
3.Test of degree of Bleaching
4.Test of Degree of Mercerising
Testing of Effective desizing in Textile processing
First we will consider ,what is desizing in Textile Processing.
The size which is applied on the warp yarn before weaving
must be removed prior to scouring for efficient scouring and
bleaching later.
The removal of size i.e.desizing, is therefore, the first operation
in fabric preparation.Desizing can be carried out by using
acids,alkalis,enzymes,hypochlorites,sodium bromite etc.
The yarns, particularly the warps running lengthways
throughout the fabric, are subjected to a high degree of
abrasion during weaving. To prevent breakage or damage of
warp yarns due to abrasion, size is imparted to the warp yarn.
The presence of size on the fabric makes it stiff and renders its
treatment difficult with different liquors used in dyeing and
finishing Therefore one of the initial step in wet processing is
the elimination of size and water soluble admixtures.The
operation being called desizing.Desizing process is very
essential to make the fabric suitable for next process.
(A)Weight loss method:
While desizing, starch is removed from the fabric. Hence, the
material will undergo weight loss after the process is over.More
the weight loss better is the efficiency of the desizing
enzymes.Weight loss can be calculated in terms of %weight
loss as follows:
% Weight Loss=(Initial gsm-final gsm)/Initial gsm*100
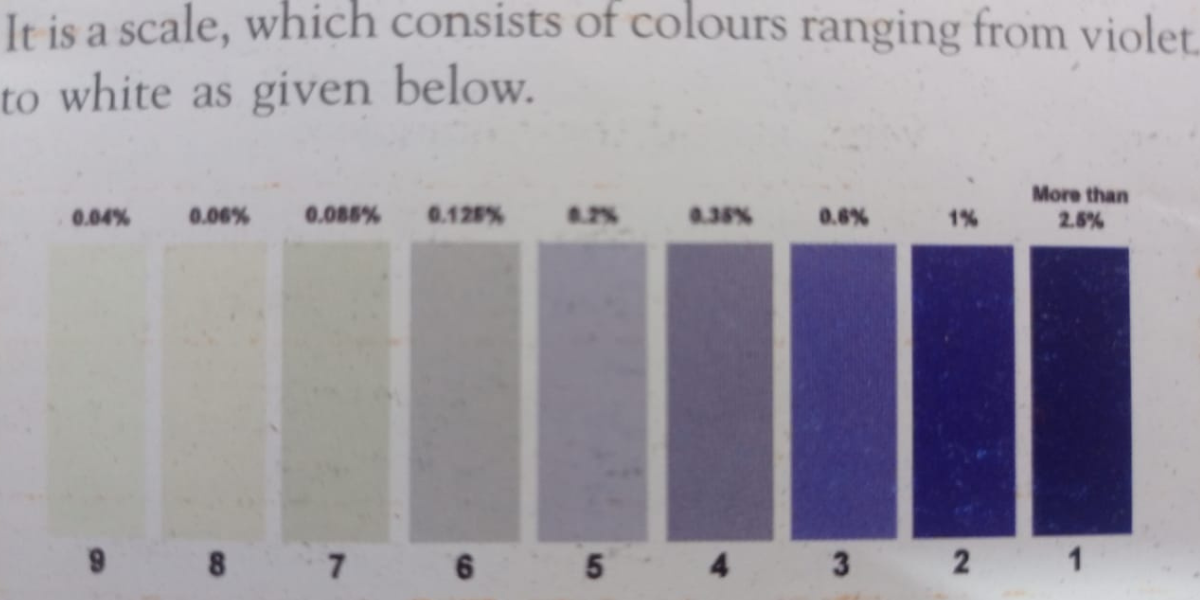
(B) Tegewa Scale method: It is scale, which consists of colours
ranging from violet to yellow as given bellow.
Reagent Preparation:
Take potassium iodide [10gm of KI (100%)] in 100 ml of water;
then add 0.6358 gm of iodine (100%); stir well until iodine is
completely dissolved in the KI solution. After this, add 800 ml
of ethanol.
Then by adding water the volume should be .raised to 1000 ml.
We will check this by click on method of testing of desizing.
Test of Effective Scouring in Textile Processing

First we will discuss what is scouring:
Normally natural fiber contains dust, oil, wax, minerals and
manyimpurities as well. we have to clean these for further
process. So theway of removing those impurities is called
scouring. The mostimportant wet process used on textile
products before dyeing or printing is scouring.Main purpose of
cotton scouring is to eliminate natural and artificial
impurities from the fabric, making it cleaner and more
absorbent.
Cotton fabric scouring is a chemical cleaning procedure that
removes natural wax and non-fibrous impurities from the
fabrics, as well as any additional soiling or dirt. Cotton fabric is
usually scoured in kiers,which are large iron vessel.
Drop Test Method
Properly scoured fabric should wet out faster and be more
water absorbent.This test method to use to measure fabric
wetting.A drop of water is placed on the fabric and the time it
takes for the drop topenetrate the fabric is recorded.The faster
the wetting time,The more absorbent is the fabric.
Please click on link for Prodcedure.
Drave's Test Method
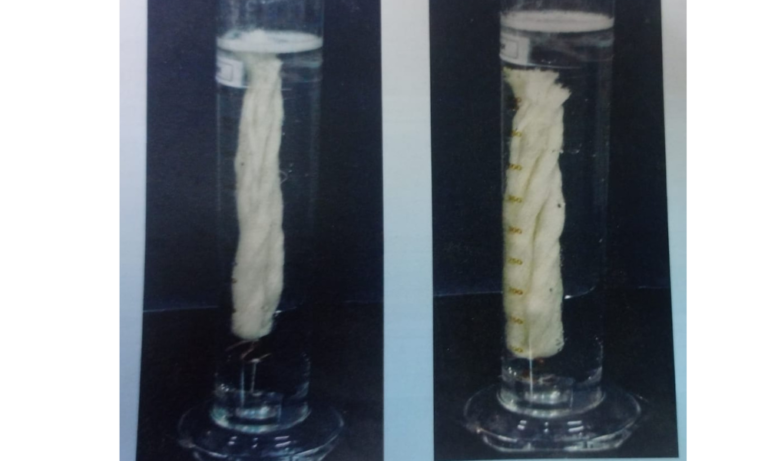
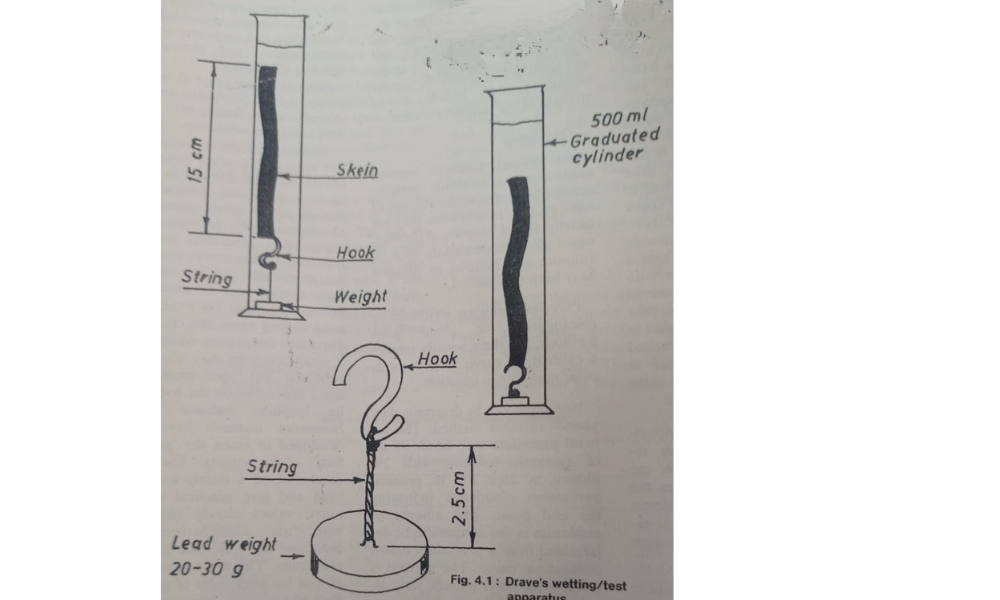
The wetting efficiency of wetting agents can be compared by
using Drave’s test of Canvas disc test.In Drave;s test ,a
standard skein of grey cotton yarn(5gm)is held submerged in
the test solution by means of a weight.As the solution wet the
yarn,air is progressively displaced and the buoyancy decreases
until.,at the end point of test the skein sinks.The time interval
between the immersion of the skein and when it definitely starts
to sink is noted as the sinking time.A 5 gm skein of grey two ply
cotton yarn is folded to form a loop of About 15 cm in
diameter,and a short length of copper wire is passed
round at any point along the circumference and fastened by
Hooking the bent ends together.To the middle of the wire is
attached a small weight ,so adjusted that the weight and wire
combined weight exactly 4.5 g.This is known as the sinker.This
is attached by a strong fine mercerised cotton thread to the
anchor,a piece of load weighing 20-30 g. The sinker and
anchor must be 2.5 cm apart.
The canvas disc test is very similar in principle to the drave’s
test but Uses a woven fabric in the form of a canvas disc in
place of the yarn.
Test of degree of Bleaching

Testing of Bleaching=A process of whitening fibers or fabrics or depriving a coloured
material is called Bleaching. This is brought about by using various bleaching-
agents. Generally chlorine is used for cotton and other
vegetable fibres and peroxide and sulphur dioxide for animal
fibres.
A.Fluidity of dispersion of cellulose from bleached cotton cloth
B.Reflectance ,blue and whiteness of bleached fabrics are the main
test used to determine the effectiveness of Testing of bleaching.
Hypochlorite bleaching
Hypochlorites as bleaching agents are still popular despite the anti-chlorine
lobby and environmental pressures. Some of these salts which are used for
the bleaching of textiles are Calcium hypochlorite (Bleaching powder), Sodium
hypochlorite, Lithium hypochlorite and chlorinated trisodium phosphate etc.
Peroxide bleaching
Hydrogen peroxide was discovered in 1818 and its use in bleaching textiles
was first suggested in 1866. However, its high cost limited its use in cotton
bleaching until 1935. The problem was partially solved by the process using
barium peroxide and phosphoric acid. In 1926 hydrogen peroxide was
manufactured by an electrolytic process based on the decomposition of
persulphuric acid (H2SO4).
Advantages and Disadvantages of Peroxide over Hypochlorite Bleaching
Advantages
1.Peroxide is an universal bleaching agent and can be employed for wool,
silk as well as cotton. It is especially suited to the bleaching of union fabrics
containing both cotton and wool or silk.
2.Hydrogen peroxide is a milder reagent than hypochlorite and the degrading effect of peroxide bleaching on cellulose is less influenced than is the case with hypochlorite.
3.Peroxide is capable of continuing the scouring action simultaneously with the bleaching action, thus a single stage combined scour and bleach or a continuous method is possible using hydrogen peroxide.
4.Peroxide bleaching is in general less liable to have adverse effect on dyed threads. The white effect is good and permanent and there is less risk of yellowing at a later stage.
5.Thorough rinsing followed by scouring or antichlor treatment is required with hypochlorite bleaching, whereas with peroxide a comparatively short rinsing suffices.
6.With hydrogen peroxide, there is no danger of equipment corrosion, no unpleasant odours and no limitations as to processing techniques.
7.Increasing strict control over the discharge of AOX from chlorine bleaching liquors has led to a greater advantage of peroxide processes for bleaching cellulosic fibres.
Disadvantages
1.Bleaching with peroxide is costlier than that of hypochlorite or bleaching powder.
2.Hydrogen peroxide bleaching requires stabilization usually with silicates which brings the risk of forming resist stains in ubsequent dyeing, and causes a build-up of hard crystalline deposits on plant and machinery causing abrasion damage to the fabric during passage.
3.‘Catalytic damage’ occurs during hydrogen peroxide bleaching of cotton fabrics and results in small spots of unevenly dyed fabric or even, in severe cases, the formation of small holes.
4.There is limitation in white obtained on acrylic fibers. It also causes deleterious effect on skin when used in a concentrated form.